Diabetes
Staying Healthy During Ramadan
Ramadan is finally here. Millions of Muslims are observing fasting from morning twilight to the evening twilight which lasts for approximately 15 hours a day for one whole month in Bangladesh. During the holy month of Ramadan, people get together to break the fast with rich food with high calories. Some may also engage in less physical activity du...
Decoding Diabetes: Causes, Types, and Effective Management
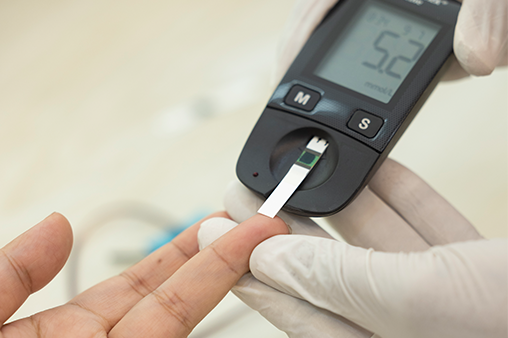
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects millions of people worldwide and has become a significant global health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the prevalence of diabetes has been steadily increasing, making it crucial for individuals to understand this condition and its management...